SUSTAINABLE BIO-PHARMA MANUFACTURING FOR TOMORROW

CAPSULE
Conceptual Product Solutions
Team: Laurenz Simonis, Marian Dembkiewicz
Duration: 10 weeks (2022)
Collaboration partner:

Context
CAPSULE represents a paradigm shift in bio-pharma manufacturing, designed to inspire a sustainable transformation in industry processes. By adopting a modular and energy-efficient approach, CAPSULE reorganises the conventional bio-pharma manufacturing processes, allowing for quick adaptability to shifts in production capacities and emerging markets.
Design Brief
CAPSULE was a 10-week collaboration between Cytiva and the Umeå Institute of Design. Cytiva offers tools, products, and services for biopharmaceutical research and manufacturing. As a pivotal player in bio-pharma research and manufacturing, Cytiva recognizes the need for differentiators beyond technology specifications in a maturing landscape. With a commitment to having the 'Human at the core' and being 'Dynamically modern,' Cytiva tasked us with crafting future-ready solutions through best-in-class end-to-end User Experience Design. Beyond a user-centric approach, the challenge extended to creating sustainable solutions for the next generation of disposable products.
What is Chromatography?
In biopharmaceutical manufacturing, chromatography serves as a critical technique for separating and purifying biomolecules. The intricate process involves the installation of single-use components on chromatography machines to control the flow of processed solutions within a meticulously maintained cleanroom environment to prevent contamination.
The Overarching Problem
The process heavily relies on single-use items, which require packaging them in multiple protective layers and extensive use of disinfectants to avoid contamination. We identified that there is a way to make this process more sustainable by strategically rethinking the logistics.

What are Cleanrooms?
Cleanrooms are controlled environments within the manufacturing or scientific research field where airborne particles, such as dust, microbes, and other contaminants, are kept within strict limits. These specialized rooms are designed to maintain low pollutants to ensure the quality and integrity of sensitive processes. Cleanrooms are commonly used in pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics manufacturing, and aerospace industries, where even tiny particles can negatively impact product quality or research outcomes. The level of cleanliness in a cleanroom is defined by the number of particles per cubic meter at a specified particle size. Maintaining these conditions in cleanrooms involves specialized air filtration systems, controlled airflow, and stringent personnel attire and behaviour protocols.
The Cleanroom operators are responsible for assembling, inspecting, testing, and unpacking equipment, tools, and devices used in clean rooms. Their essential functions are:
- Clean, prepare, and assemble products
- Operate the equipment
- Inspect and track parts and processes during production
- Ensure the quality of the final product
- Maintain the work area in a clean and orderly condition
- Report defective material or questionable conditions
- Contribute and adhere to safety and quality
- Communicate the operation status in a timely manner
The current workflow requires the operators to go linearly through multiple levels of cleanroom to reach the highest-grade cleanroom where the chromatography machines are located. In each room, they have to remove a layer of the packaging of the single-use items till they get to the highest-grade room where they install these items.

Work-flow Problem Identification

No hands for identification
Managing the flow kit and batch protocol leaves no hands for additional tasks.

Forgetting items or tools
Moving items into the cleanroom involves multiple steps, with the risk of leaving them in a previous room.

The walk of shame
Forgetting or dropping tools needs redressing, sanitizing, and returning to the buffer room.
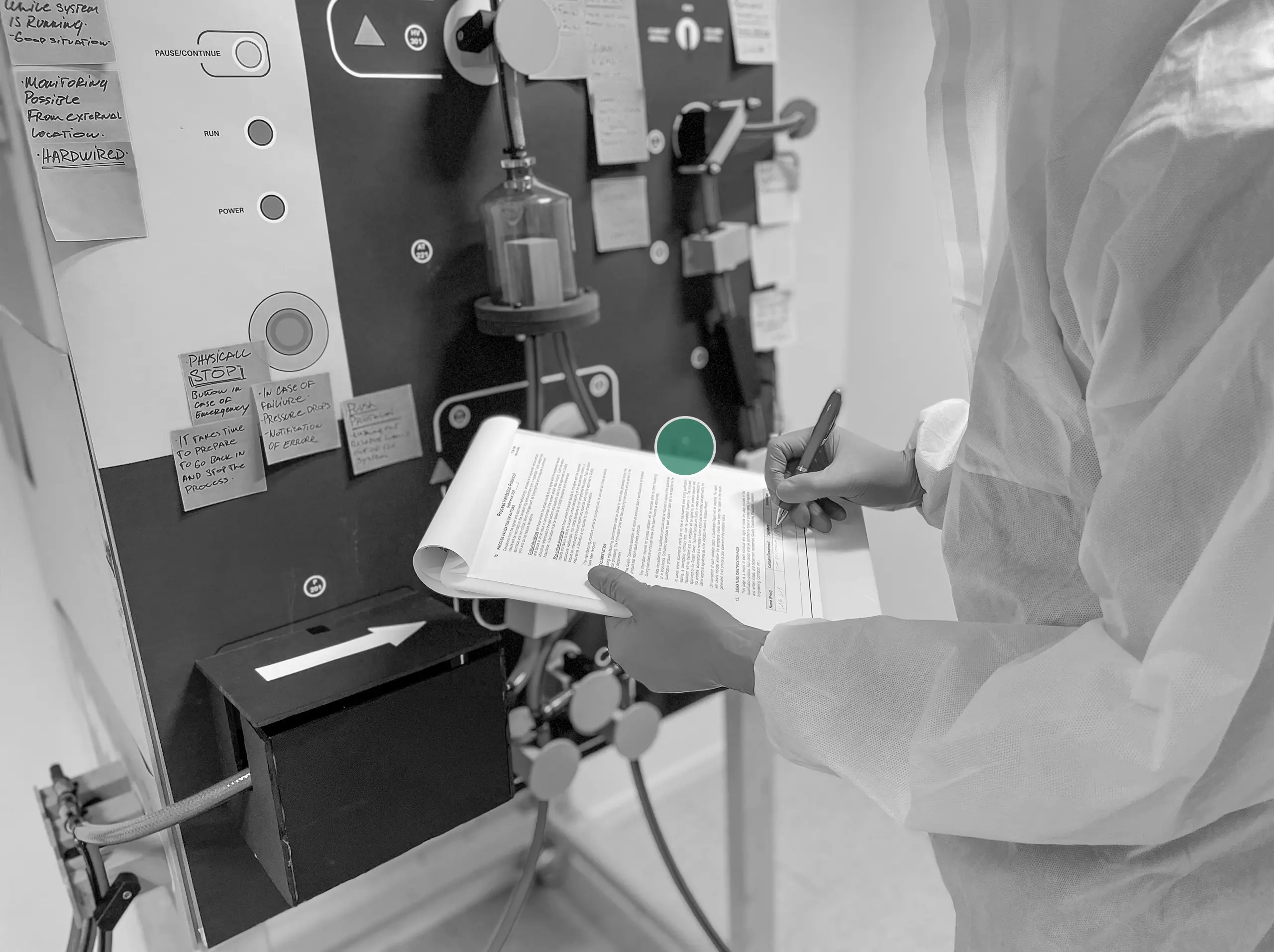

Inefficient batch-protocol
Manually filling in the batch protocol is time-consuming and allows for human error.
Defining our strategic approach
Approximately 30% of staff time is spent on documentation-related activities
Human accuracy is 91% in regard to manual tasks within the documentation
Average asset utilisation in Pharma (OEE) is as low as 35%
Through research, we gathered that...
1. The digitalisation of operations in biopharma manufacturing holds great potential to increase overall equipment efficiency.
2. Biopharma is moving towards precision medicine, which calls for scalable and flexible manufacturing.
3. The UN Sustainable Development Goals require companies to take greater responsibility for the whole lifecycle of their products.
...and asked ourselves,
"How might we envision the role of equipment providers in this evolving industry, and what are the implications for the cleanrooms of the future?"
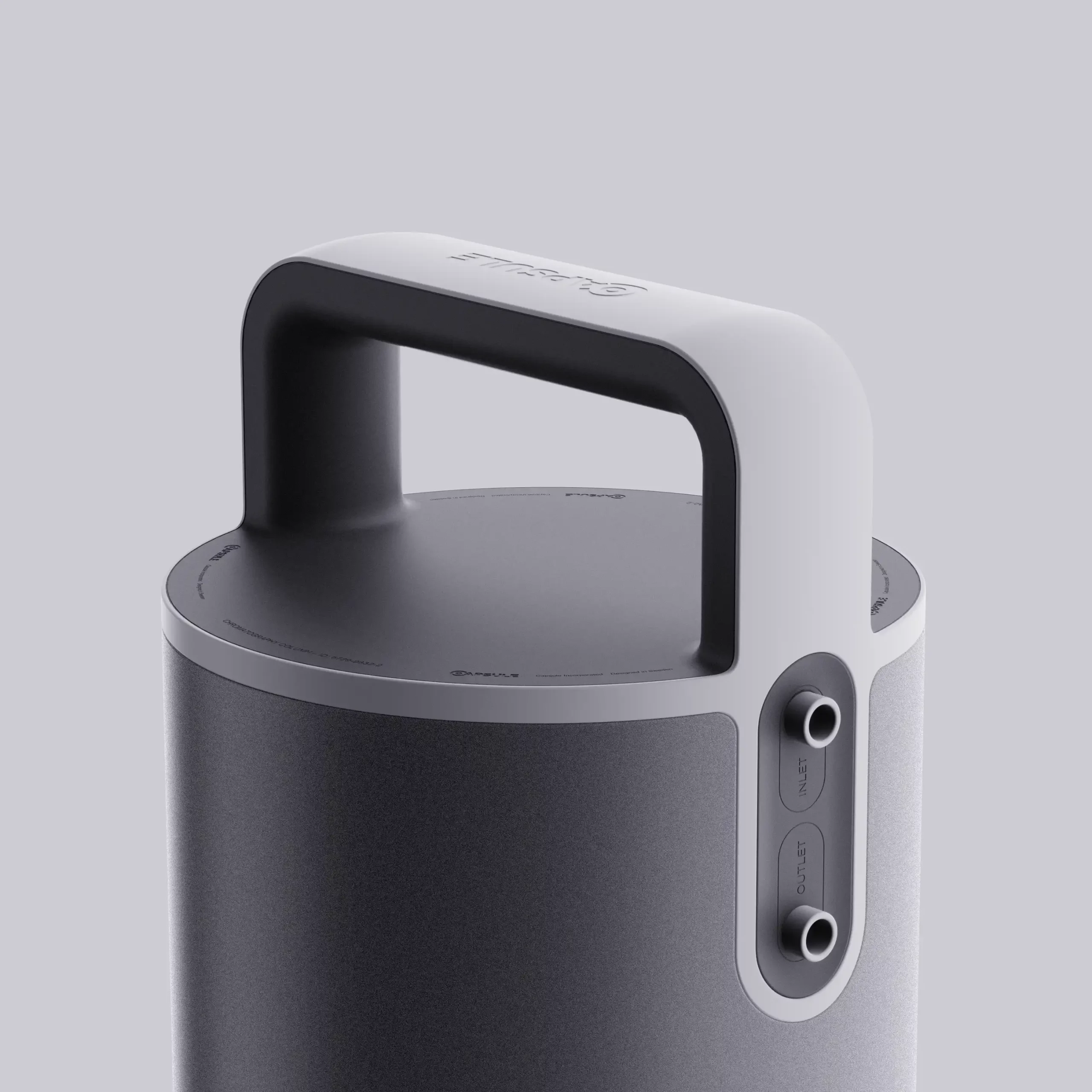
Introducing CAPSULE


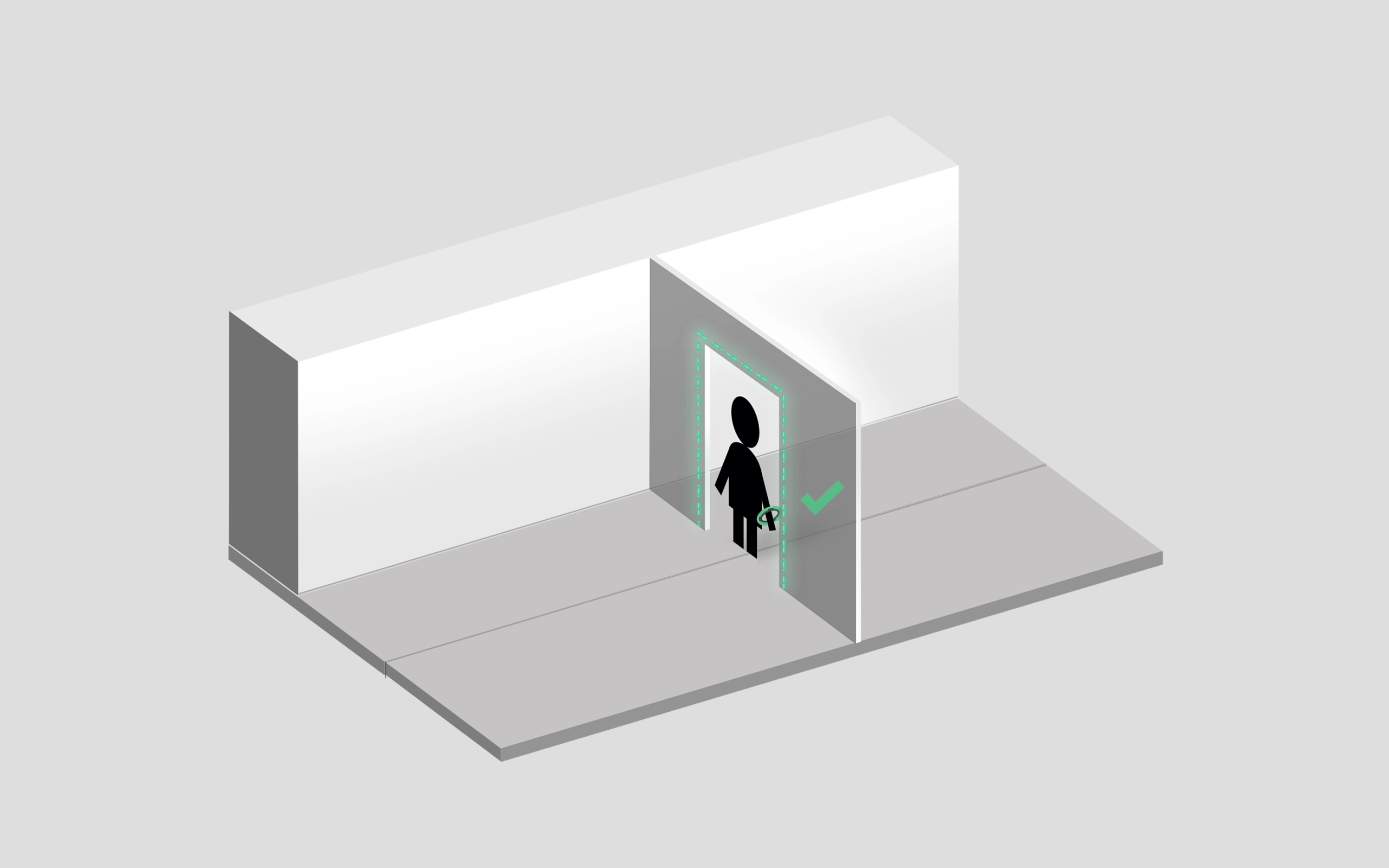
Aseptic Hatch System
The Aseptic Hatch System is the core of our new setup. It allows seamless delivery of single-use components crucial for bio-pharma manufacturing directly into the highest-grade cleanrooms. With hatches that connect supply areas to cleanrooms, we ensure the integrity of operations, preventing exposure to impurities for precision and efficiency.



Wall-integrated Machines
The machines are integrated into the walls, lowering energy consumption by only placing sensitive processes in the highest-grade cleanroom. During maintenance, the cleanroom workflow always runs without disruptions as repairs happen in the maintenance access from the back of the machines. Reducing the downtime of these machines and cleanrooms can increase the Average Asset Utilisation in Pharma.


New Work-flow for Operators
Automatic authorisation
The Capsule band authorises operators at cleanroom doors.

Lights ON!
The Capsule band also enables resource optimisation.


Vibration and light feedback
The band can guide the operators to machines that need attention.


Digitised operations to aid the operators
Presently, a substantial amount of staff time is spent on documentation-related activities inside cleanrooms. We have digitised manual tasks like filling up the batch protocol by integrating them with the digital interface of our new machines.


The service side
The service side offers access to single-use components directly in the cleanroom and disposal of such, being taken care of by Capsule staff and ensuring full control over the product lifecycle.

Workspace and retreat areas
Due to the more compact layout, some space can be used for either working or recreational setups, the latter using more natural colours and lighting to offer operators a retreat during downtimes in the cleanroom, aiming to improve well-being.



How does this benefit the environment?
More efficient use of equipment will lower energy consumption and reduce the overall amount of machines needed to provide the same output
New cleanroom design requires less energy to run by only placing sensitive processes in the highest-grade cleanroom
Taking responsibility for the whole product lifecycle of single-use products, according to UN Sustainable Development Goals
Process


Selected Works

Rescusci CartGraduation Project (Solo)

pebbleStrategic Product Design (Team)

IMPRNTNew Tools for Crime Scene Investigators (Solo)

Design Language SystemHardware design language exploration for Laerdal

HORIZONSound Design (Team)

XO driverProduct Construction and Analysis (Solo)

EVionElectric Charger for the Indian Context (Solo)